Beautiful Tips About Is Wi-Fi Duplex Or Half-duplex

Difference Between HalfDuplex Vs FullDuplex Total Phase
Understanding Wi-Fi Communication
1. The Need for Speed (and Clarity!) in Wi-Fi
Ever wondered how your phone, laptop, and smart fridge all manage to chatter away on the same Wi-Fi network without everything grinding to a halt? It's not magic, though sometimes it feels that way. The key to understanding this is figuring out whether Wi-Fi is duplex or half-duplex. The answer, as with most things in the tech world, is a little more nuanced than a simple yes or no. But don't worry, we'll break it down! Think of it like this: is your Wi-Fi router a polite conversationalist, or does it hog the spotlight?
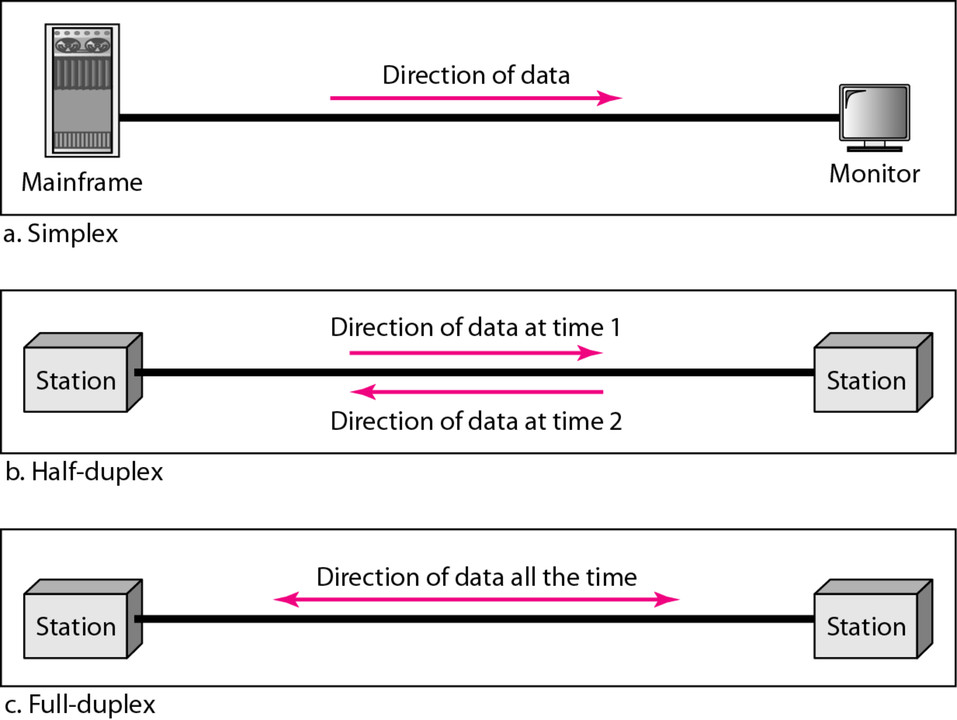
The short answer, technically speaking, is that older Wi-Fi standards (like 802.11b/g/a) primarily used a half-duplex communication method. But modern Wi-Fi (802.11n/ac/ax, also known as Wi-Fi 4/5/6) has evolved and incorporates features that allow for something closer to full-duplex. It's more accurate to say that modern Wi-Fi aims for full-duplex-like performance even though the underlying technology still has half-duplex roots.
This improved performance is achieved through clever techniques. Think of it like a highly efficient traffic controller directing data streams, minimizing collisions and maximizing throughput. Essentially, the newer standards introduce efficiencies that cleverly work around the limitations of the underlying half-duplex system. It's like taking a one-lane road and building passing zones everywhere — you still only have one lane, but you can get a lot more traffic through!
So, while the physical radio waves themselves might be bouncing around in a half-duplex manner at the most fundamental level, the experience for the user is much closer to full-duplex, allowing for simultaneous sending and receiving of data, improving your video calls, online gaming, and general internet surfing.

Simplex Half Duplex E Full
Diving Deeper
2. The Talkie-Walkie Analogy
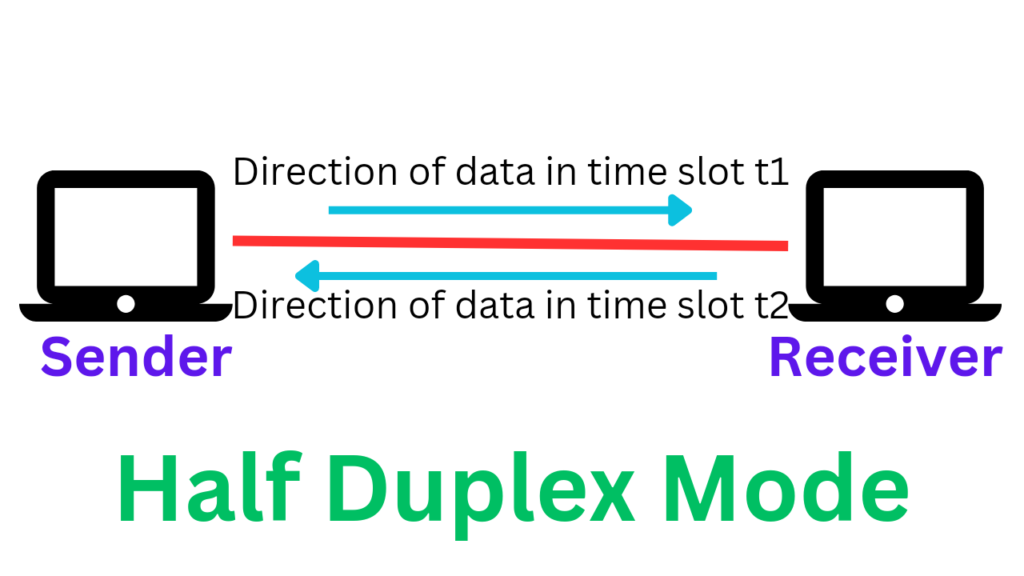
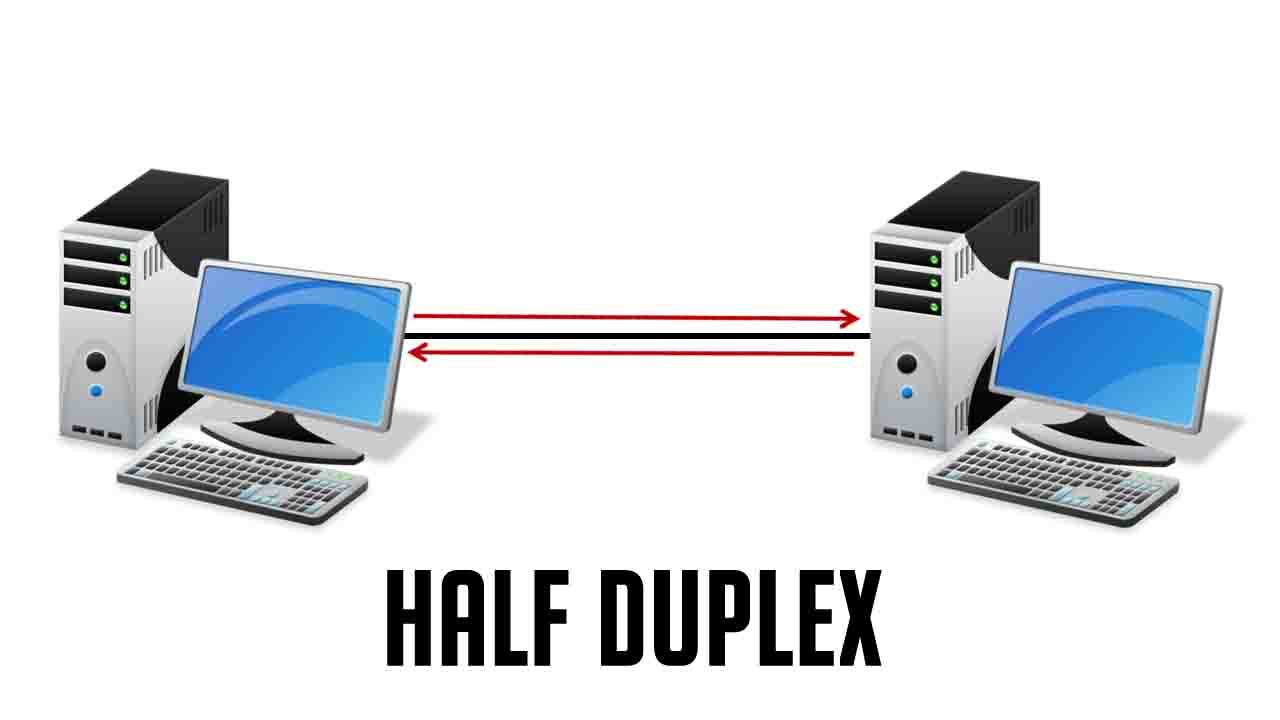
Imagine a walkie-talkie. You can either talk or listen, but not both at the same time. Thats half-duplex in a nutshell. In the context of Wi-Fi, half-duplex means that a device can either transmit data or receive data, but it can't do both simultaneously on the same channel. This is because the transmitting and receiving happen on the same frequency.
Think of it like a single-lane bridge. Only one car can cross at a time. If two cars try to cross from opposite directions, theyll crash (or, in Wi-Fi terms, experience a collision). When a collision occurs, the data needs to be re-transmitted, which slows things down. It is also very annoying.
Early Wi-Fi standards relied heavily on this half-duplex method. Devices would "listen" to the channel before transmitting to make sure no one else was talking. If the channel was clear, they'd transmit their data. If not, they'd wait a random amount of time and try again. This waiting and re-transmitting added overhead and limited the overall speed and efficiency of the network.
The problem with this system is obvious. The more devices you have on the network, the more likely collisions become, and the slower everything gets. It's like trying to have a conversation at a crowded party where everyone is shouting over each other. That is why modern wifi evolved for efficiency.
Full-Duplex (The Ideal Scenario) and Modern Wi-Fi's Tricks
3. Speaking and Listening at the Same Time
Full-duplex, on the other hand, is like a phone call. You can talk and listen simultaneously. In networking terms, this means a device can transmit and receive data at the same time without collisions. This significantly increases the efficiency and speed of the network.
Modern Wi-Fi standards don't achieve true full-duplex in the purest sense of the word, but they get pretty darn close through clever techniques like MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) and MU-MIMO (Multi-User MIMO). These technologies use multiple antennas to transmit and receive data simultaneously, effectively creating multiple pathways for data to flow. It's similar to turning that single-lane bridge into a multi-lane highway.
MIMO, for example, allows a router to send and receive data to multiple devices at the same time, using different spatial streams. This is like having multiple conversations simultaneously by using different frequencies of your voice (though, thankfully, Wi-Fi is a lot better at this than people are). MU-MIMO takes this a step further by allowing the router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously instead of sequentially. In the past a router would be focused on one device at a time before moving on to the next, but MU-MIMO enables it to send information to more devices.
These advanced techniques significantly reduce the chances of collisions and improve the overall performance of the Wi-Fi network. While the underlying technology might still have half-duplex characteristics, the result is a much faster and more efficient experience that feels very much like full-duplex. Its the best of both worlds; backward compatibility and a modern feel.

The Role of Channels and Frequency Bands
4. Choosing the Right Lane on the Wi-Fi Highway
Wi-Fi operates on different channels within specific frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz). These channels act like lanes on a highway, allowing devices to communicate without interfering with each other. Choosing the right channel can significantly impact the performance of your Wi-Fi network.
Think of it this way: if everyone is crammed into the same lane (channel), things will get congested and slow down. By spreading devices across multiple channels, you can alleviate congestion and improve performance. Most modern routers can automatically select the best channel, but it's still a good idea to check and make sure it's not overcrowded. There are apps that let you analyze your wifi channel traffic and see how congested it is.
The 5 GHz band generally offers more channels and less interference than the 2.4 GHz band, making it a better choice for devices that require high bandwidth, such as streaming videos or playing online games. However, the 5 GHz band has a shorter range than the 2.4 GHz band, so it may not be suitable for devices that are located far from the router. Often, newer routers will have two networks running and connect devices to the ideal one for the devices purpose.
So, while the duplex nature of Wi-Fi is important, the channel and frequency band also play a crucial role in determining the overall performance of your network. It's all about optimizing the various aspects of your Wi-Fi setup to ensure the smoothest and fastest possible experience. Finding the best configurations will help to keep the wifi running smoothly.
Simplex Half Duplex E Full REVOEDUCA
Practical Implications
5. Making the Most of Your Wireless Network
Understanding the duplex (or near-duplex) nature of Wi-Fi and the impact of channels and frequency bands can help you optimize your network for better performance. What does this look like in the real world?
First, consider upgrading to a modern router that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards (802.11ac or 802.11ax). These routers utilize MIMO and MU-MIMO technologies to improve efficiency and reduce collisions. Also, consider a mesh system! This type of system expands coverage and allows for a more efficient flow of traffic.
Second, analyze your Wi-Fi channels and choose the least congested one. Many Wi-Fi analyzer apps are available for smartphones and computers that can help you identify the best channel. Some routers can do this automatically. Furthermore, ensure that you position your router in a central location, away from obstacles that can interfere with the signal.
Finally, consider using a wired connection for devices that require the highest bandwidth and lowest latency, such as gaming consoles or streaming devices. A wired connection eliminates the potential for collisions and interference, providing a more stable and reliable connection. Even consider splitting traffic by prioritizing the devices that need the most bandwidth.
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still scratching your head? Let's tackle some common questions about Wi-Fi and its duplex nature.
Q: Does the number of devices connected to my Wi-Fi affect its duplex performance?A: Absolutely! The more devices connected, the more contention for the available bandwidth, which can lead to increased collisions and reduced performance, especially with older half-duplex-focused standards. Modern routers with MU-MIMO can handle multiple devices more efficiently, but there's still a limit. It depends on how those devices are being used, as well. More devices can overload it quickly.
Q: Is there a way to force my router to use full-duplex mode?A: While you can't directly force a router into "full-duplex mode" in the traditional sense, you can optimize its settings to mimic full-duplex performance. This includes enabling MIMO/MU-MIMO, selecting the optimal channel, and prioritizing traffic for certain devices. The settings that you would need to enable are often on by default, so there might not be anything you need to change.
Q: If Wi-Fi isn't truly full-duplex, why is it so much faster than older wireless technologies?A: Because of the clever techniques like MIMO, MU-MIMO, and channel bonding that modern Wi-Fi standards employ. These technologies significantly improve efficiency and reduce collisions, resulting in a much faster and more reliable connection. It's like taking a horse and buggy and upgrading to a sports car — same basic principle (transportation), but vastly different performance!