Top Notch Tips About Is 6GHz Shorter Than 5GHz

Decoding the GHz Mystery
1. Frequency and Wavelength
Ever wondered what those GHz numbers mean on your router? Simply put, GHz (gigahertz) measures frequency. Think of frequency as how many waves pass a point in a second. Now, heres the kicker: frequency and wavelength are like two sides of the same coin, always working inversely. Higher frequency means shorter wavelength, and vice versa. So, the quick answer to the core of our article — "Is 6GHz shorter than 5GHz?" — is a resounding yes!
Now, why should you even care? Well, understanding this relationship can significantly impact your Wi-Fi experience. Wavelength dictates how well a signal penetrates walls and other obstacles. Shorter wavelengths (like those of 6GHz) tend to have a harder time passing through solid objects compared to longer wavelengths (like those of 5GHz). It's a bit like trying to squeeze a beach ball through a keyhole — not the easiest task.
But before you write off 6GHz entirely, hold your horses! The shorter wavelength also has its advantages, which we'll explore in the upcoming sections. It's not always about brute force penetration; sometimes, finesse and less congestion can win the day.
Ultimately, choosing between 5GHz and 6GHz isn't about one being strictly "better" than the other. It's about understanding their strengths and weaknesses and selecting the frequency band that best suits your specific needs and environment. Think of it like choosing the right tool for the job — a hammer isn't always the best choice for delicate work!

Why Shorter Isn't Always Worse
2. Less Crowded Airwaves
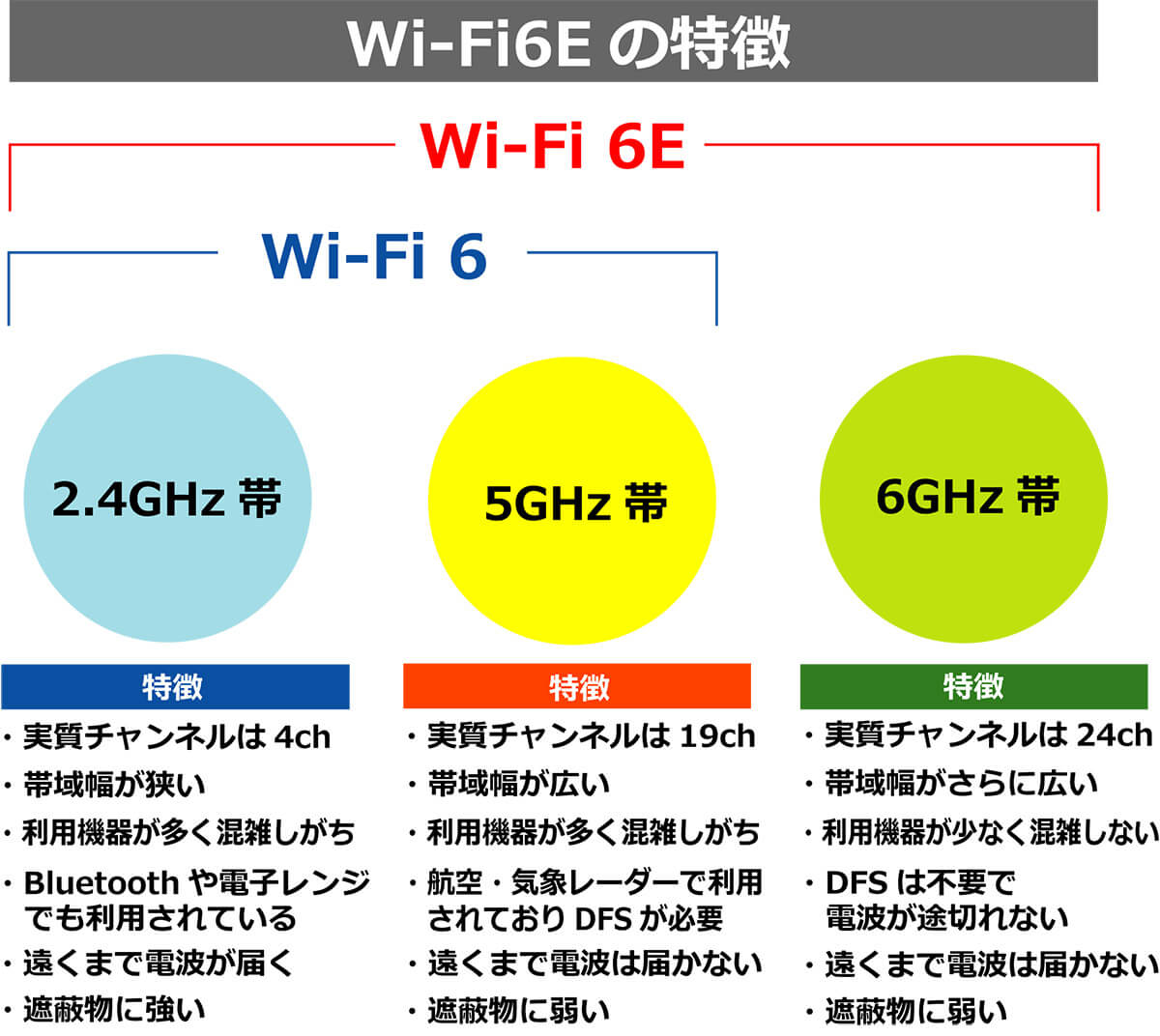
Imagine a crowded concert venue versus a spacious outdoor arena. 5GHz, while offering decent range, has become increasingly congested. This is because more devices are using it, leading to potential interference and slower speeds. Think of it like rush hour on the highway — everyone's trying to get somewhere, but progress is slow and frustrating.
Enter 6GHz, the new kid on the block. It operates on a less crowded spectrum, meaning fewer devices are competing for bandwidth. This translates to potentially faster speeds and more reliable connections, especially in densely populated areas or homes with many connected devices. It's like finding a secret shortcut through the city, bypassing all the traffic jams.
The availability of more channels in the 6 GHz band is a major advantage. It means less interference from your neighbors' Wi-Fi networks, and a smoother, more stable connection for your devices. It also offers the possibility for wider channels (160MHz), which can increase the potential data throughput, resulting in faster download and upload speeds.
So, while the signal may not travel as far or penetrate walls as effectively as 5GHz, the cleaner airwaves of 6GHz can provide a superior experience in the right conditions. It's like choosing a smaller, faster car over a large, lumbering truck — sometimes speed and agility are more important than sheer size.

The Trade-Off
3. Weighing Your Options
When deciding between 5GHz and 6GHz, you're essentially trading off range for speed and reduced congestion. 5GHz offers a better range and can penetrate walls more effectively, making it suitable for larger homes or areas with significant obstructions. However, it's also more prone to interference and congestion.
6GHz, on the other hand, offers faster speeds and less congestion but has a shorter range and struggles with wall penetration. This makes it ideal for smaller apartments or homes where devices are relatively close to the router. Also perfect if you want to use it for high bandwidth consuming activities such as VR.
Consider your specific needs and environment when making your choice. If you live in a large house with thick walls and need Wi-Fi coverage throughout, 5GHz might be the better option. If you live in a small apartment with a fast internet connection and want to maximize speed and minimize latency, 6GHz could be the way to go.
Think about the devices you'll be using and how you'll be using them. Gaming, streaming high-definition video, and video conferencing all benefit from faster speeds and lower latency, making 6GHz a good choice. General web browsing and email may not require the same level of performance, so 5GHz could be sufficient.

The Truth About WiFi 6E (and Why You Might Not Want To Upgrade
Making the Most of 6GHz
4. Optimizing Your Setup
To get the most out of 6GHz, consider placing your router in a central location, free from obstructions. This will help maximize the signal range and minimize interference. Experiment with different router placements to find the sweet spot that provides the best coverage and performance.
Ensure that your devices are compatible with 6GHz. Not all devices support the 6GHz band, so check the specifications of your smartphones, laptops, and other connected devices. Upgrading to 6GHz-compatible devices can unlock the full potential of your Wi-Fi network.
Keep your router's firmware up to date. Manufacturers regularly release firmware updates that improve performance, security, and compatibility. Installing the latest firmware can help optimize your 6GHz connection and resolve any potential issues.
Consider using a mesh Wi-Fi system. Mesh systems use multiple nodes to create a seamless Wi-Fi network, extending coverage throughout your home. Mesh systems with 6GHz support can provide excellent performance and coverage, even in larger homes with obstructions. Place the additional nodes where you might have coverage issue for maximum performance.
The Future of Wi-Fi
5. The Evolution Continues
6GHz is the latest evolution in Wi-Fi technology, offering significant improvements in speed, capacity, and reduced congestion. As more devices and networks adopt 6GHz, it's poised to become the dominant Wi-Fi band in the coming years. But the evolution doesn't stop there.
Researchers are already exploring even higher frequency bands, such as millimeter wave (mmWave), for future Wi-Fi technologies. These higher frequencies offer even greater bandwidth and lower latency, but they also have even shorter ranges and are more susceptible to interference. This might be in your next smartphone.
The future of Wi-Fi is likely to involve a combination of different frequency bands, each optimized for specific use cases. 6GHz will continue to play a crucial role in providing fast and reliable connectivity for a wide range of devices and applications.
So, while "Is 6GHz shorter than 5GHz" seems like a simple question, it opens the door to understanding the complex and ever-evolving world of Wi-Fi technology. Embrace the advancements, experiment with different configurations, and enjoy the benefits of faster and more reliable wireless connectivity.

FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Let's tackle some frequently asked questions about 6GHz to clear up any lingering confusion.
7. Q
A: It depends. If your older devices support 5GHz or 2.4GHz, they will still connect to your router, as most 6GHz routers are dual-band or tri-band. However, they won't be able to utilize the 6GHz band's faster speeds and lower congestion. Only devices specifically designed with 6E or Wi-Fi 6E will be able to take full advantage of this standard.
8. Q
A: Potentially, yes! Wi-Fi 6E which uses 6 GHz band, can achieve speeds that rival or even surpass Gigabit Ethernet, especially under ideal conditions. However, wired Ethernet still offers more consistent and reliable performance, particularly in environments with a lot of interference.
9. Q
A: Check the product specifications of your router. Look for terms like "Wi-Fi 6E," "6GHz support," or "tri-band router." The router's packaging or web interface should also indicate whether it supports the 6GHz band. If you're unsure, consult the manufacturer's website or contact their support team.